Introduction: A Legacy of Challenging the Chip Giants
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) has long been known for its ability to challenge industry giants and make its mark in the highly competitive semiconductor space. Founded in 1969 by Jerry Sanders, the company began with the goal of producing innovative chips to rival the dominance of established players like Intel. Over the years, AMD has carved out a niche as a key competitor in the CPU and GPU markets, earning a reputation for offering performance alternatives at more affordable prices.
Despite facing significant challenges, including fierce competition from Intel and financial hurdles, AMD’s commitment to technological innovation has helped it gain a loyal customer base and achieve major milestones. Today, AMD continues to push boundaries in computing, offering powerful solutions for everything from gaming and consumer desktops to enterprise data centers. The company’s journey is one of resilience, creativity, and a relentless drive to innovate.
The Founding and Early Years of AMD
AMD was founded in 1969 by Jerry Sanders, a former Fairchild Semiconductor executive, who envisioned a company that could challenge industry giants and bring innovative solutions to the semiconductor space. The company started with a focus on producing memory chips and logic components, serving primarily as a supplier to the larger semiconductor players of the time. AMD’s early years were characterized by the struggle to differentiate itself in a market dominated by companies like Intel, Texas Instruments, and Fairchild.
In its early days, AMD faced many financial and technical challenges. One of the major difficulties was competing with Intel, a company that had established a strong foothold in the microprocessor market. However, AMD’s persistence and aggressive strategy soon began to pay off. In the mid-1970s, AMD secured a significant deal with Intel by licensing the rights to produce Intel’s microprocessor designs, specifically the 4004 microprocessor, which marked the beginning of its foray into the processor market.
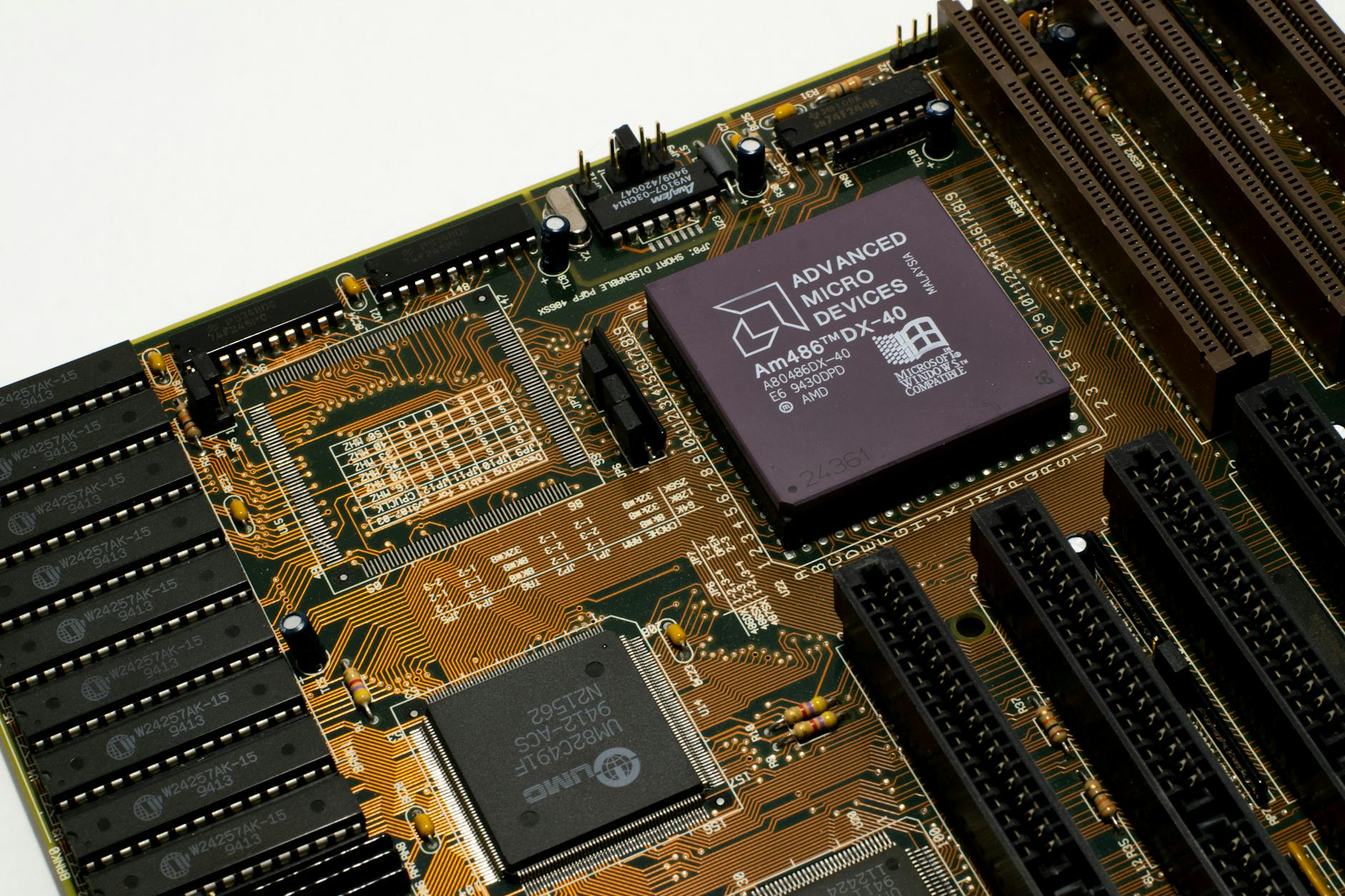
This move proved to be a turning point for AMD, as it gained access to Intel’s established technologies and built its own brand by offering competitive alternatives. During this period, AMD also ventured into producing its own chip designs, including the AM386, which was introduced in 1985. The AM386 was a significant step for AMD, as it offered a product that was compatible with Intel’s 80386 microprocessor while being more affordable. This allowed AMD to position itself as an affordable alternative to Intel’s high-cost solutions, and the success of the AM386 helped AMD gain more recognition in the semiconductor market.
As the 1980s progressed, AMD continued to expand its product line and diversify its offerings. The company introduced the AM486, which competed directly with Intel’s 80486 processor, and began building relationships with PC manufacturers. By the early 1990s, AMD’s market share was growing steadily, and it was clear that the company was no longer just a challenger, but a legitimate contender in the semiconductor industry. AMD’s ability to provide high-performance chips at lower prices than Intel made it a popular choice among computer enthusiasts and businesses alike.
Despite the growing competition from Intel, AMD’s focus on innovation and delivering value for money allowed it to thrive during the 1990s, setting the stage for its future success.
AMD vs. Intel: The Competitive Landscape
The rivalry between AMD and Intel has been one of the most defining aspects of the semiconductor industry. For years, Intel maintained a dominant position in the microprocessor market, controlling a vast majority of the personal computer processor market. However, AMD’s strategy of providing alternative, affordable solutions has allowed it to continuously challenge Intel’s market share, resulting in an ongoing battle for supremacy in the CPU space.
The roots of the rivalry can be traced back to the 1980s when AMD initially emerged as a competitor by licensing Intel’s technology. However, the real competition between the two companies began to take shape in the late 1990s and early 2000s. By this time, Intel had become the uncontested leader in the microprocessor market, with its Pentium processors achieving widespread adoption in personal computers. AMD, on the other hand, was still considered the underdog, albeit one with significant potential.
The year 2000 marked a major turning point for AMD. The company released its Athlon processor, based on the K7 architecture, which was a significant leap forward in performance compared to Intel’s Pentium III and Pentium 4 processors. The Athlon outperformed Intel’s chips in several benchmarks, providing consumers with a more powerful and affordable alternative. This success established AMD as a credible competitor to Intel, marking the beginning of a fierce rivalry between the two companies that would define the next two decades.
Intel, unable to ignore AMD’s growing success, responded by releasing a new generation of processors, including the Pentium 4, which aimed to outperform the Athlon. However, AMD’s competitive edge remained strong due to its focus on delivering products that offered better performance at a lower cost. The battle between the two companies escalated further when AMD released its dual-core Athlon 64 X2 processors in 2005, while Intel struggled to keep up with the trend toward multi-core processors.
In addition to their competitive product launches, AMD and Intel were also embroiled in a series of legal battles. In 2005, AMD filed a lawsuit against Intel, accusing the company of using its market dominance to suppress competition by offering rebates and other incentives to computer manufacturers in exchange for exclusive use of Intel processors. The case, which eventually led to a settlement in 2009, further highlighted the intense competition between the two companies.
Despite this fierce rivalry, AMD’s resilience in continuing to innovate and provide affordable alternatives to Intel’s high-priced processors has allowed it to remain a strong competitor. AMD’s willingness to challenge Intel on both the technological and pricing fronts has helped the company maintain a significant presence in the market.

AMD’s Technological Innovations and Key Milestones
AMD has long been recognized for its technological innovations, which have not only challenged its competitors but also helped shape the semiconductor industry. The company has introduced numerous groundbreaking products and technologies over the years, including the development of the first 64-bit consumer processor and the shift to multi-core processing.
One of AMD’s earliest breakthroughs was the launch of the Athlon 64 processor in 2003. The Athlon 64 was the first processor to support 64-bit computing for consumer desktops, a major advancement at the time. This innovation allowed computers to access larger amounts of memory and perform tasks more efficiently, which was particularly important for users working with demanding applications such as video editing and 3D rendering. The success of the Athlon 64 solidified AMD’s position as a legitimate alternative to Intel, which at the time was still relying on 32-bit processors.
In addition to its advancements in 64-bit computing, AMD made significant strides in multi-core processing. In 2005, the company released its dual-core Athlon 64 X2 processors, which offered significant improvements in multitasking and parallel processing capabilities. The move to multi-core processors was a critical moment in the evolution of computing, as it allowed for improved performance in both consumer and enterprise applications. AMD’s early adoption of multi-core technology allowed the company to stay ahead of Intel, which initially struggled to launch its own multi-core processors.
AMD’s innovations didn’t stop there. In 2017, the company released its Ryzen processors, which were based on the new Zen architecture. The Ryzen chips offered significant improvements in both performance and energy efficiency, surpassing Intel’s offerings in many benchmarks. Ryzen’s success not only reasserted AMD’s position as a serious competitor in the CPU market but also marked a turning point in AMD’s fortunes, allowing the company to recapture market share from Intel after years of competition.
AMD has also made strides in the graphics processing unit (GPU) market with its Radeon line of graphics cards. Radeon GPUs have gained significant popularity among gamers and professionals, competing directly with Nvidia’s GeForce line. The company’s focus on delivering high-performance graphics at affordable prices has made Radeon a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers and businesses alike.
Overall, AMD’s commitment to innovation has played a crucial role in its success. The company’s ability to stay ahead of the curve in terms of performance, efficiency, and cost has allowed it to challenge Intel and Nvidia while delivering high-quality products to its customers.
The Future of AMD: Embracing New Technologies and the Next Frontier
Looking ahead, AMD is positioning itself for continued success by embracing new technologies and entering emerging markets. The company has already established itself as a major player in the CPU and GPU markets, and its future growth will likely be driven by advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud computing.
One of AMD’s major areas of focus in recent years has been the data center market. In 2017, the company launched its EPYC processors, which are designed for high-performance computing in servers and data centers. EPYC processors have been met with significant success, offering performance comparable to Intel’s Xeon processors at a lower price point. As cloud computing continues to grow and the demand for data processing power increases, AMD’s EPYC chips are well-positioned to capture a larger share of the data center market.
Additionally, AMD has made significant investments in AI and machine learning. The company has already integrated AI capabilities into its CPUs and GPUs, enabling faster processing and more efficient computation for AI tasks. As AI continues to evolve, AMD’s ability to develop cutting-edge solutions for AI and machine learning workloads will play a key role in its continued success.
Another area where AMD is making strides is the gaming industry. The company’s Ryzen processors and Radeon graphics cards have become increasingly popular among gamers, thanks to their strong performance and affordability. AMD’s focus on delivering powerful yet cost-effective gaming solutions has made it a popular choice for both casual and competitive gamers. The company’s partnerships with major gaming console manufacturers, such as Sony and Microsoft, further solidify its position in the gaming space.
Finally, AMD is also making moves into the 5G market. The company’s expertise in semiconductor design and its ability to produce high-performance chips make it well-suited to support the growth of 5G technology. As the world transitions to 5G networks, AMD’s contributions to the development of the next generation of wireless technology will likely become more significant.
Conclusion
AMD’s history is a testament to its resilience and commitment to innovation. Despite facing fierce competition from industry giants like Intel and Nvidia, the company has carved out a successful niche in the semiconductor industry. From its early struggles to its recent successes with Ryzen and EPYC, AMD has shown that it is capable of competing at the highest levels of performance and efficiency.
Looking to the future, AMD’s focus on emerging technologies and its continued drive to innovate ensures that the company will remain a key player in the rapidly evolving tech landscape. As the demand for high-performance computing, AI, and cloud-based solutions grows, AMD’s contributions will likely continue to shape the future of computing for years to come.
AMD’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of semiconductor technology positions it to thrive in the face of competition, solidifying its place in the annals of the industry’s history.









